Centralized vs. Decentralized Crypto Exchanges
In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrency, the battle between decentralized and centralized exchanges has been raging on like a fierce crypto-tsunami. As a true believer in the transformative power of blockchain technology, exploring the pros and cons of these two types of exchanges is essential for navigating the crypto-verse like a pro. Get ready to have your mind blown as we unravel the mysteries behind these digital asset powerhouses and discover which one reigns supreme in the quest for financial freedom and security. Whether you’re a seasoned crypto-veteran or a curious newbie, this article will arm you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions and take your crypto game to the next level. So, buckle up and get ready for a wild ride through the exhilarating landscape of decentralized and centralized crypto exchanges!

Centralized Crypto Exchanges
Definition and Key Characteristics
Centralized crypto exchange is a digital platform controlled by a central entity that acts as a middleman between buyers and sellers.
A centralized exchange (CEX) holds digital assets for clients, facilitates crypto trading, and sets the trading terms and conditions.
Centralized exchanges have some cool features. For one, they keep the private keys to their clients’ wallets, which is super important for cryptocurrency transfers.
They usually make users go through a Know Your Customer (KYC) process. This is to follow the rules and make sure everyone is who they say they are, helping to stop things like money laundering and terrorist financing.
The process involves filling out your identity info, sending in verification documents, and waiting for them to be checked. Once that’s done, you can fund your account and start trading.
Centralized exchanges also use order book matching tech to make trading happen. This system matches buy and sell orders to facilitate trades. Plus, many of these exchanges use market makers to provide liquidity for listed cryptocurrencies, keeping the spreads competitive.
Advantages
Centralized exchanges come with a bunch of perks. First off, they’re super user-friendly, making it easy for both newbies and pros to navigate, deposit, and withdraw funds.
They also usually offer a wider range of cryptocurrencies than decentralized exchanges, which is great for diversifying your investments.
When it comes to liquidity, centralized exchanges have the edge. This means you can buy or sell assets quickly without messing up the market price, which is perfect for fast, low-volatility trades. The high liquidity comes from having a big pool of buyers and sellers and access to regulated market makers. Plus, some of these exchanges offer trading in asset derivatives like options and futures, which also boosts liquidity.
Another big plus is that many centralized exchanges are owned by regulated entities, so they’re under strict regulatory oversight. This makes them more appealing to institutional investors and professional traders who need that extra level of security and compliance.
Disadvantages
Centralized exchanges have some big downsides. One major issue is that users don’t control their own crypto wallet keys, so they don’t have direct access to their assets. This can lead to big losses if an unregulated exchange suddenly shuts down.
Security is another big problem. Centralized exchanges have been hacked many times, resulting in the loss of hundreds of millions of dollars in crypto. Hackers often target these central points of failure, making them vulnerable to attacks and scams like rug pulls, which can wipe out investors’ money.
Additionally, many centralized exchanges are run by regulated entities, meaning they’re under strict rules from regulatory authorities. These authorities can impose tough restrictions, like new licensing requirements and compliance regulations, which can limit the exchange’s ability to support certain tokens or serve users in specific areas.
Examples
Some popular centralized crypto exchanges are Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Huobi. These platforms are well-known for trading cryptocurrencies, offering lots of trading pairs, easy-to-use interfaces, and advanced trading features.
Decentralized Crypto Exchanges (DEXs)
Definition and Key Characteristics
A decentralized cryptocurrency exchange is a platform built on a decentralized, non-custodial blockchain system that mainly supports direct peer-to-peer transactions.
They let users trade directly with each other using peer-to-peer trading. Everything is controlled by self-executing blockchain apps called smart contracts.
This means there are no middlemen involved. Plus, decentralized exchanges don’t make you go through a KYC process, so you can trade anonymously.
What about private keys? On decentralized exchanges, you keep control of your private keys, making you responsible for the security of your funds.
Advantages
DEXs have some great benefits. They don’t have KYC requirements, making them censorship-resistant and perfect for users who want to trade anonymously. This also helps unbanked users who can’t access traditional banking services.
DeFi platforms, built for blockchain-based financial services, let users lend and borrow funds through a peer-to-peer system. Smart contracts control lending pools, allowing users to lend funds and earn interest. Users can also earn passive income through DeFi staking, which involves locking up crypto assets to validate transactions on proof-of-stake systems and earning rewards.
Another big plus is that DEXs have lower transaction fees since they enable direct transactions between buyers and sellers without intermediaries.
Disadvantages
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have some downsides. They often have lower liquidity than centralized exchanges (CEXs) due to a smaller user base and trading volume. This can cause significant price deviations, leading to less favorable trades.
DEXs are also more technical and require some blockchain knowledge. Users need compatible wallets and must manage their private keys. They also have to buy native platform tokens to pay for gas fees, which usually means buying specific cryptocurrencies on CEXs first.
These steps can be tricky, especially for beginners, and mistakes can lead to asset losses. Additionally, DEXs aren’t regulated like CEXs, which means they don’t have to follow strict rules like AML and KYC protocols. This makes them more vulnerable to illegal activities, such as money laundering, making regulated companies wary of them.
Lastly, DEXs often lack customer support, which can be a big challenge for users who need help.
Examples
Some popular decentralized crypto exchanges are Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap, and dYdX. These DEXs are well-liked in the crypto community for their non-custodial trading, liquidity pool systems, and the ability to trade a wide variety of ERC-20 tokens.
Comparison of Centralized and Decentralized Exchanges
Security
DEXs have an edge over CEXs in security because they don’t hold users’ assets, reducing the risk of hacks and theft. However, CEXs are improving their security with features like multi-factor authentication, cold storage, and insurance funds to protect users’ assets.
Liquidity
CEXs usually have higher liquidity than DEXs since they attract more users and handle more trades. This higher liquidity means faster trade execution and better prices. But as DEXs become more popular, the liquidity gap between them and CEXs is expected to close.
User Experience
CEXs offer a more user-friendly experience with intuitive interfaces and advanced trading features, making them easier for beginners. DEXs can be more complex, requiring users to interact with smart contracts and navigate more complicated interfaces.
Fees
Both CEXs and DEXs charge fees, but CEXs often have higher trading fees to cover platform maintenance, customer support, and regulatory compliance. DEXs typically have lower fees since they have fewer overhead costs, but they may have higher gas fees for blockchain transactions.
Regulatory Compliance
CEXs are heavily regulated and must comply with KYC and AML requirements, which can provide legitimacy and security but may limit privacy and result in account restrictions. DEXs, being decentralized, offer more privacy and freedom in trading but lack regulation, which can attract illicit activities and raise concerns with authorities.
Comparative Table
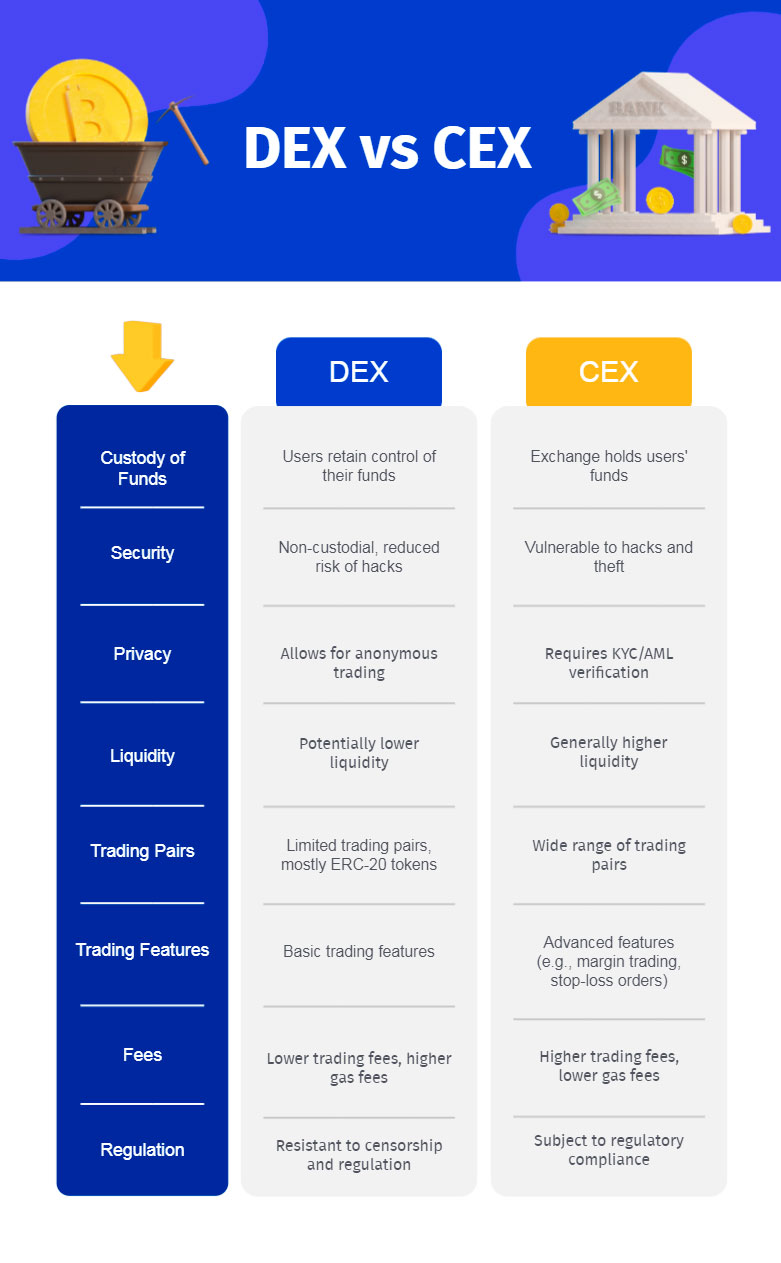
Summarizing
There’s no clear winner between centralized and decentralized exchanges – it’s all about what you prefer. Some traders might like CEXs better, while others might go for DEXs. In fact, many traders use both. Certain tokens are only available on DEXs, and CEXs are great for getting in and out of crypto and the regular financial system.










